The US has recently imposed tariffs on imports from countries like Canada, Mexico, and China, increasing consumer retail prices. These tariffs affect various products, including electronics and everyday goods. Major retailers such as Target and Best Buy have indicated that these new tariffs are prompting price hikes, sparking consumer interest in understanding how tariffs influence retail prices (WTTW News).
Source: NapkinFinance
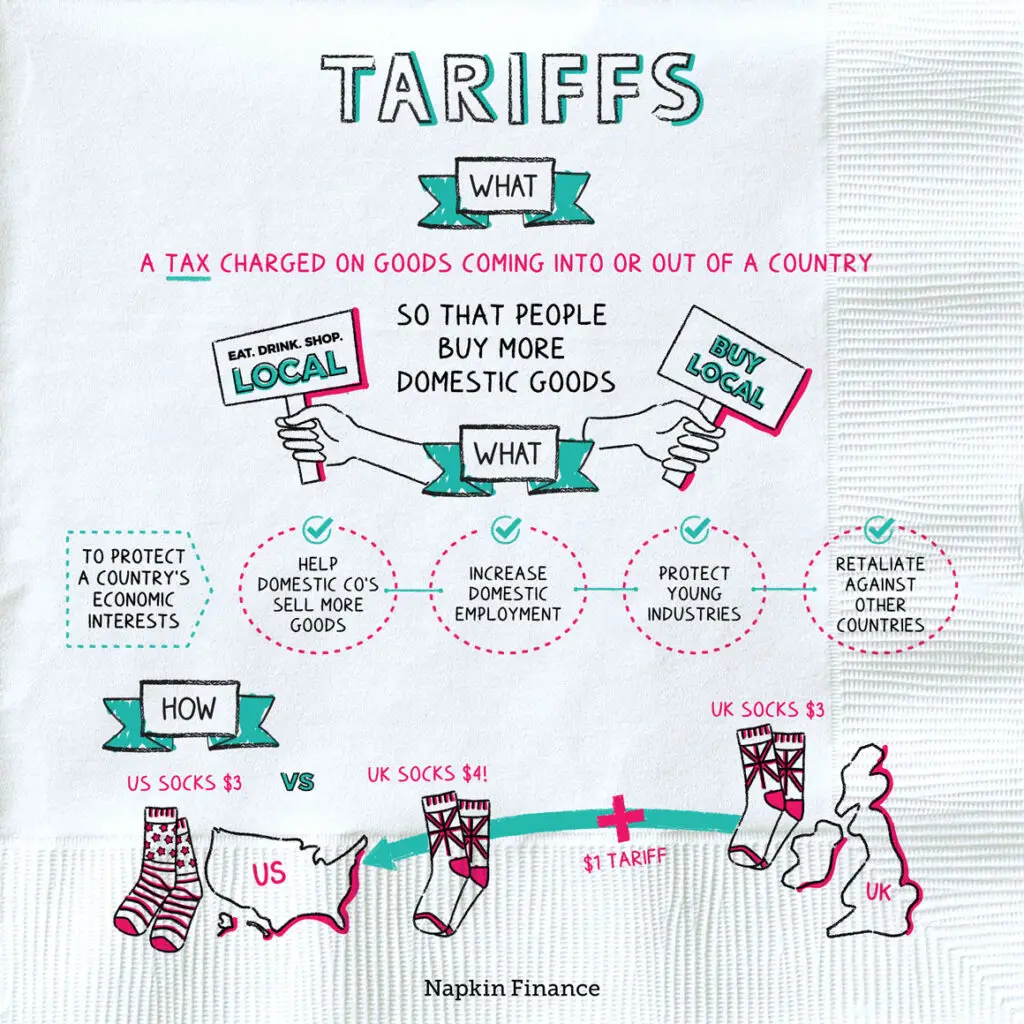
Why Is the US Imposing Tariffs?
A tariff is a tax placed on imported goods. Countries impose tariffs for several reasons, including:
- Protecting Domestic Industries – Tariffs make imported goods more expensive, encouraging consumers to buy locally produced items. This protects domestic businesses from foreign competition.
- Reducing Trade Deficits – If a country imports more than it exports, it has a trade deficit. Tariffs can reduce imports and boost domestic production, helping to balance trade.
- Political and Economic Leverage – Tariffs can be used to pressure other countries into changing their trade policies. For example, the US has imposed tariffs on China to address concerns over unfair trade practices.
- Generating Government Revenue – Since tariffs act as taxes on imports, they bring in money for the government, which can be used for infrastructure and public services.
Why Is the US Targeting China & the EU?
The US has imposed tariffs on Chinese and EU goods for several reasons:
- To address unfair trade practices – The US accuses China of intellectual property theft, forced technology transfers, and government subsidies that create unfair competition. Similarly, trade disputes with the EU have arisen over subsidies in key industries, such as aerospace and agriculture, leading to retaliatory tariffs.
- To reduce reliance on foreign imports – By making goods from China and the EU more expensive, the US aims to encourage domestic manufacturing and sourcing from other regions.
- To negotiate better trade deals – Tariffs serve as leverage to push both China and the EU toward trade agreements that the US views as fairer.
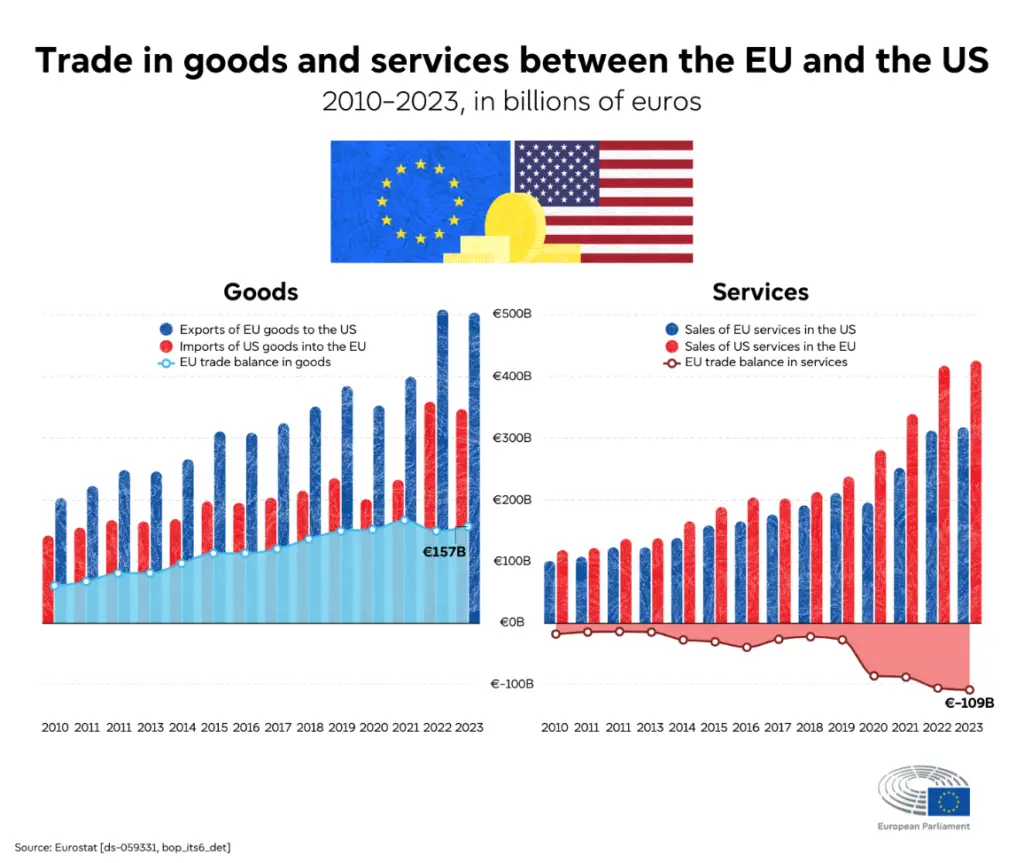
During the Trump administration, the US placed 25% tariffs on $250 billion worth of Chinese goods, including electronics, furniture, and clothing (Wikipedia). The US has also engaged in trade disputes with the EU, particularly in sectors such as technology, agriculture, and digital services, affecting transatlantic trade relations. Recent data shows that while the EU enjoys a trade surplus in goods with the US (€157 billion in 2023), it faces a growing trade deficit in services (€-109 billion), highlighting the evolving nature of economic competition between the two blocs.
Source: Europal
How Do Tariffs Affect Retail Prices?
When tariffs are imposed on imported goods, retailers and manufacturers often pass these costs onto consumers, leading to higher retail prices on store shelves.
Some of the industries most affected by tariffs include:
- Electronics – Many products like smartphones, laptops, and televisions rely on Chinese-made components. Tariffs on these imports make devices more expensive.
- Automotive – Tariffs on steel, aluminum, and auto parts drive up the cost of cars and repairs.
- Agriculture – Retaliatory tariffs from China on US agricultural products reduce exports, affecting farmers and increasing grocery prices.
How Can Retailers Minimize the Impact of Tariffs?
Retailers can implement several strategies to reduce the burden of tariffs on both their businesses and consumers:
- Diversifying Supply Chains – Sourcing products from other countries that aren’t subject to tariffs can lower costs.
- Negotiating with Suppliers – Retailers can work with suppliers to share the burden of increased costs.
- Investing in Domestic Production – Moving manufacturing to the US can reduce reliance on imported goods.
- Offering Consumer Incentives – Loyalty programs, discounts, and flexible payment options can help customers manage rising prices.
Leveraging Dynamic Pricing and Content Capabilities
Retailers can utilize SaaS automation tools such as dynamic pricing and dynamic content capabilities to adapt to tariff-induced price fluctuations:
- Dynamic Pricing: This strategy involves adjusting prices in real-time based on factors like demand, competition, and cost changes. By implementing dynamic pricing, retailers can respond swiftly to tariff-related cost increases, optimizing profitability while remaining competitive.
- Dynamic Content: Tailoring online content based on user behavior and preferences allows retailers to highlight alternative products or promotions, steering consumers toward items less affected by tariffs. This personalized approach can maintain sales volumes and customer satisfaction.
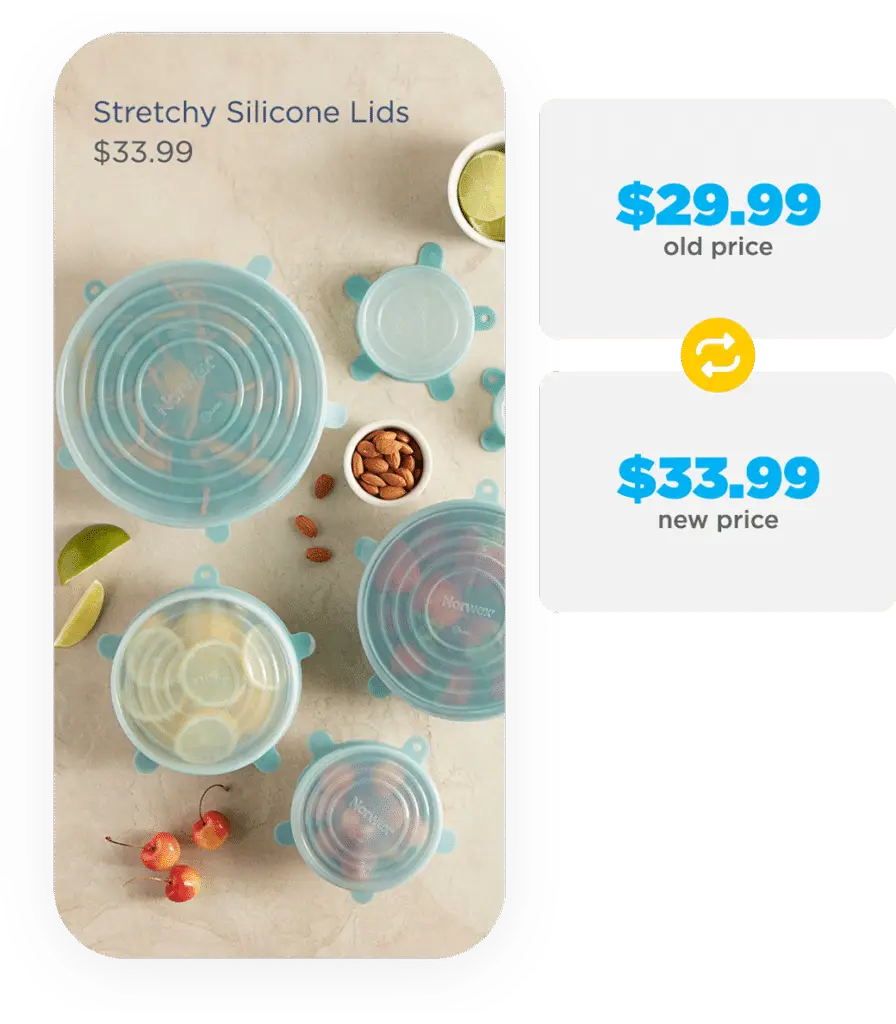
How Can Retailers Communicate Tariff Increases Without Losing Customers?
Since price hikes can frustrate consumers, retailers must strategically communicate tariff-driven cost increases. Here’s how:
- Be Transparent – Explain to customers why prices are rising without blaming the government or other countries.
- Educate Consumers – Use newsletters, social media, and in-store signage to inform customers about tariff impacts.
- Highlight Value Over Price – Emphasize the quality, durability, and benefits of products rather than just the cost.
- Offer Affordable Alternatives – Provide budget-friendly options to cater to cost-conscious shoppers.
Adapting and absorbing the impact of tariffs
Tariffs play a crucial role in trade policy but have direct consequences for consumers and retailers. While they are designed to protect domestic industries, tariffs often result in higher retail prices and disrupt supply chains.
Retailers must adapt by diversifying supply chains, leveraging pricing strategies, and effectively communicating with customers to manage the effects of tariffs. Consumers, in turn, may need to explore alternative products or purchasing options to navigate the rising costs.


